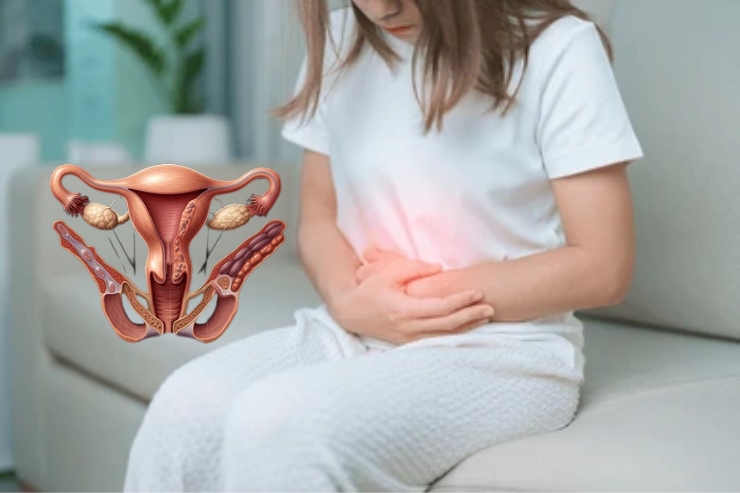
Endometriosis is a chronic gynecological condition where the tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (endometrium) starts growing outside the uterus. These abnormal growths can appear on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, outer surface of the uterus, bladder, intestines, and even in distant parts of the body. Each month, like the normal uterine lining, these misplaced tissues respond to hormonal changes and may bleed, but unlike menstrual blood, they have no way to exit the body, leading to pain and inflammation.
Many women with endometriosis experience distressing symptoms that can significantly affect their daily life and fertility. While the severity of symptoms can vary, it’s important to seek medical care when symptoms are persistent or worsening.
Common symptoms of endometriosis include:
Pelvic pain, especially during menstruation
Heavy or irregular vaginal bleeding
Pain during or after bowel movements
Abdominal bloating, constipation, or diarrhea
Rectal bleeding during periods
Difficulty in conceiving (infertility)
Treatment and management of endometriosis depend on the severity of symptoms and fertility goals. Surgery remains the primary treatment for moderate to severe cases. Laparoscopic surgery is both a diagnostic and therapeutic approach—it helps identify the extent of the disease and remove as much of the affected tissue as possible. Pain medication and hormone therapies may offer temporary relief but have a high recurrence rate. Laparoscopic management is especially effective in reducing pain and improving fertility outcomes, making it the preferred option in many cases.

